Clause Definition with Examples
The article contains —
■ what is the meaning of Clause
■ what are types of Clause
■ Clause with examples
Definition of Clause
Clause is such a group of words that forms part of a sentence and has a Subject and a Predicate of its own, is called Clause.
Classification of Clauses
Clause is of three kinds–
(A) Principal Clause (B) Subordinate Clause (C) Co-ordinate Clause

● Definition of Principal Clause:
(A) Principal Clause
Principal Clause is the main clause of a sentence that does not depend on another clause to express its complete sense.
Examples of Principal Clause
i) I know the time when he will come.
ii) I think that you have made a mistake.
iii) Teach me how to draw pictures.
Note: In the above sentences, I know the time, I think, Teach me are the Principal Clauses because they are able to make complete sense without depending on other clause.
● Definition of Subordinate Clause:
(B) Subordinate Clause
A Subordinate Clause is called the dependent clause as it depends on the Principal Clause in a sentence.
Examples of Subordinate Clause
i) Tell me the time when he will come back.
ii) He dreamt that he would be the President of India.
iii) A student who neglects his studies can not prosper.
Note: In the above sentences, when he will come back, that he would be the President of India, who neglects his studies are the Subordinate Clauses because they are unable to make complete sense without taking help of the Principal Clause.
● Definition of Coordinate Clause:
(C) Co-ordinate Clause
A Co-ordinate Clause is one that contains two or more Principal Clauses joined together by co-ordinating conjunctions.
Examples of Co-ordinate Clauses
i) He fired the gun but it missed the target.
ii) Study your lesson carefully else you will fail in the exam.
iii) Some praise the arts and some praise the sciences.
Note: In the above examples, in every sentence there are two Principal Clauses which are joined together by co-ordinating conjunctions like but, else, and.
Now, the Subordinate Clauses are subdivided into three parts—
(A) Noun Clause (B) Adjective Clause (C) Adverbial Clause

● Definition of Noun Clause:
Noun Clause
A Noun Clause is used in a sentence in the same way as a Noun itself may be used in a sentence.
A Noun Clause is used in a sentence in the following ways —
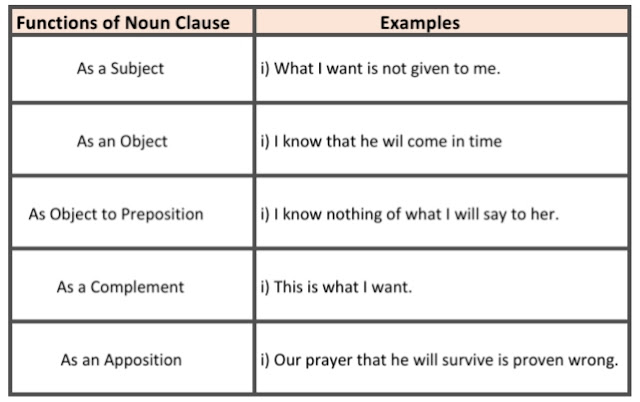
More Examples of Noun Clause
As Subject:
i) How he solved the problem is a mystery to me.
ii) That he is honest is known to all.
As Object:
i) I believed what he said.
ii) Everybody knows that he is honest.
As Object to Preposition:
i) There is no sense in what he said.
ii) The situation depends on how he will react.
As Complement:
i) The man is whom everybody wants.
ii) My desire is that he will accept me.
As an Apposition:
i) The allegation that he had stolen my purse is not believed by me.
ii) It is uncertain that he will come back in time.
● Definition of Adjective Clause:
Adjective Clause
An Adjective Clause or Relative Clause is a part of sentence that has its subject and predicate and is used as an Adjective to qualify a Noun or Pronoun.
Note: The Noun or Pronoun qualified with Adjective Clause is called Antecedent. The Adjective Clause is placed next to the Antecedent.
Linkers used in Adjective Clause
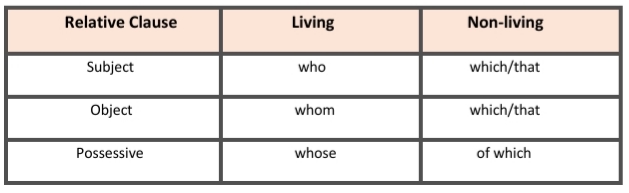
Examples of Adjective Clause
Subject:
i) This is the boy who has won the scholarship.
ii) It is the chair which is broken
Object:
i) The girl whom you saw yesterday is my sister.
ii) The pen which I lost was gifted by my father.
Possessive:
i) This is boy whose father is an advocate.
ii) This is the painting of which I have heard a lot.
● Definition of Adverb Clause:
Adverbial Clause
An Adverbial Clause is used in a sentence as an Adverb is used to modify a Verb, an Adjective or even an Adverb.
Note: An Adverbial Clause denotes — time, place, cause, result, condition, comparison, contrast, purpose.
Linkers used in Adverbial Clause
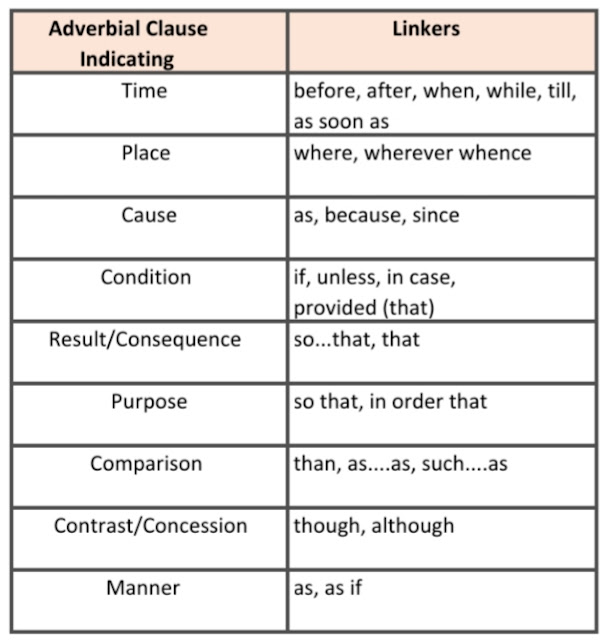
Examples of Adverbial Clause
Indicating Time:
i) I took my dinner after I completed my task.
ii) As soon as I reached home, it started raining. Indicating Place:
i) You can stay wherever you like.
ii) I have found the pen where nobody will find it.
Indicating Cause:
i) He will not pay off his debts as he is poor.
ii) I took a taxi because I wanted to reach in time.
Indicating Condition:
i) We will accept him if he behaves well.
ii) You will not succeed unless you study carefully. Indicating Results/Consequence:
i) The boy is so tiny that he can not reach there.
ii) So hot is it in summer that many died out of heat.Indicating Purpose:
i) We eat so that we may live.
ii)He works hard in order that he may succeed. Indicating Comparison:
i) I know him better than you know.
ii) He is not as tall as his sister. Indicating Contrast/Concession:
i) Though he insulted me, I remained silent.
ii) Although he tried hard, he could not complete it.Indicating Manner:
i) As you sow so you will reap.
ii) As you feel so you will act.
You May Like To Read More:
